Speed Boost and New Features in MotionBend 1.3.2
In MotionBend 1.3.2, the big news is multithreading. The three most processor intensive functions in MotionBend (tracking, motion estimation and rendering) have been rewritten to take advantage of Grand Central Dispatch.
Speed Boost
This means that if you have more than one CPU core then you will experience a speed boost. If you have N cores then you won’t get exactly an N times speed up due to the nature of multithreading. In order to execute a function in parallel, it must be broken up into subtasks that can be executed simultaneously. Then the data must be partitioned so that each subtask can work without interfering with other subtasks. The results from the separate tasks are then merged into a single result. Data partitioning and results merging creates extra work and cannot be performed simultaneously. Furthermore, some tasks cannot be executed in parallel, for example writing output frames to disk must be performed sequentially.
Multiple Event Selection
It is now possible to select multiple motion events. You might want to use this to quickly delete/merge a number of events. Click and hold down the mouse button to drag select multiple events.
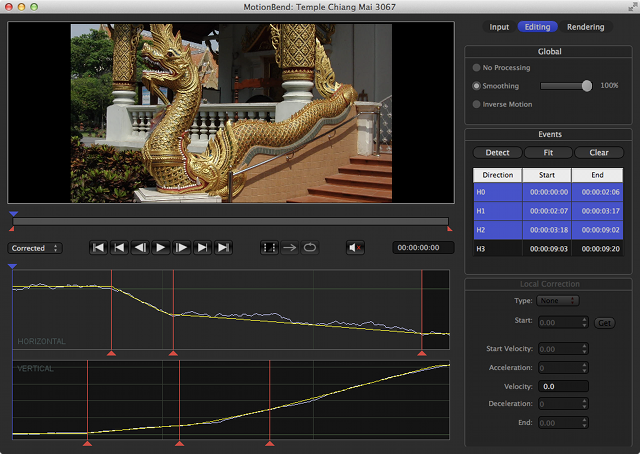
Multiple Selected Motion Events
Buffered Playback Mode
This feature reads video frames into memory so that MotionBend can playback directly from memory without reading from disk or decompressing. It is also very easy to change the direction of playback; there are 3 modes: forwards, backwards and “ping-pong” (palindromic). With forwards and backwards you can set repeat, ping-pong plays continuously until you stop.

Buffer Playback Controls
To use buffered mode, click on the RAM button and wait for frames to be stored in memory. The next two buttons are for playback mode and repeat. When video is buffered, the selection bar turns blue and the RAM image has a blue outline.

Buffered Frame Selection
In buffer mode, the frame selection only refers to the range of frames loaded into the memory buffer.